Discover 3D Scanning and 3D Reconstruction in Maintenance
3D scanning and 3D reconstruction are advanced technologies used in the field of industrial maintenance.
3D scanning allows the capture of three-dimensional digital models of real objects, while 3D reconstruction involves creating virtual models from scan data.
These technologies offer numerous benefits in terms of visualization, planning, and optimization of maintenance operations.
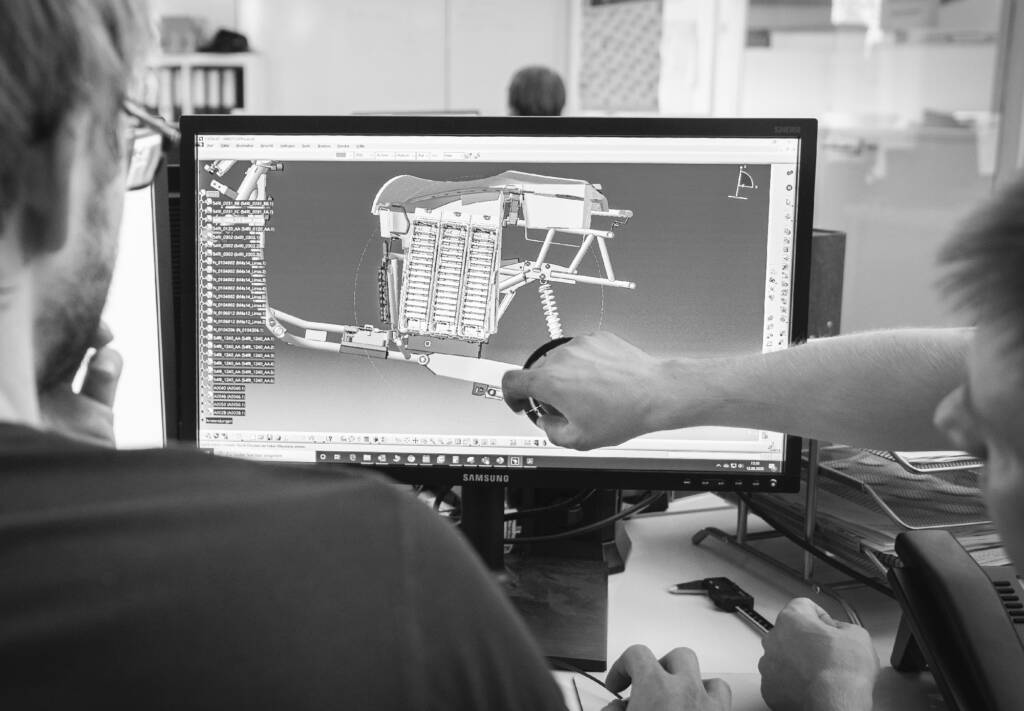

3D Scanning and 3D Reconstruction: What are they?

3D scanning is the process of capturing spatial information of a real object using laser sensors or other measurement technologies. It creates a precise three-dimensional digital model of the object by capturing millions of data points in space.
3D reconstruction then takes this scan data and converts it into a usable virtual model. This may involve creating surfaces, textures, and other features to achieve a realistic representation of the real object in a virtual environment.
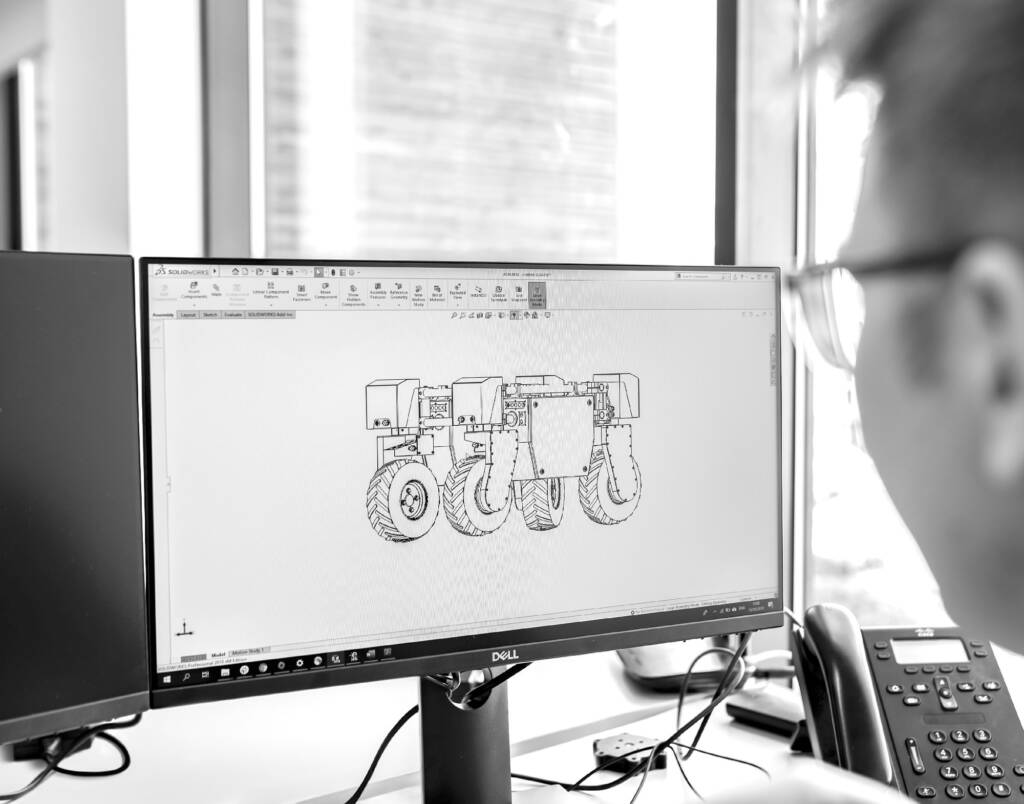
What is the relevance of these technologies in maintenance?
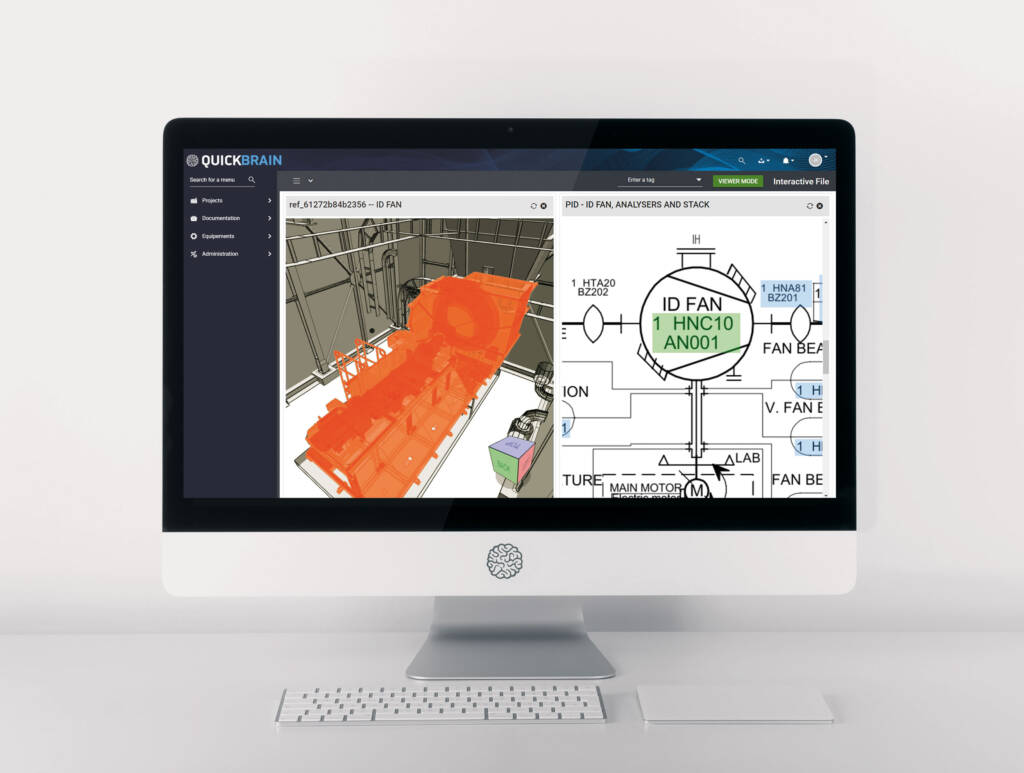
First and foremost, 3D scanning and 3D reconstruction allow for detailed visualization of objects and equipment, including complex systems and hard-to-reach spaces. This facilitates visual inspection, detection of potential issues, and precise planning of maintenance activities.
Moreover, these technologies enable virtual simulations, allowing for the evaluation of the impacts of modifications and repairs before their implementation. This is known as “digital twinning.”
In summary, 3D modeling facilitates effective information sharing among operational teams and precise intervention planning.
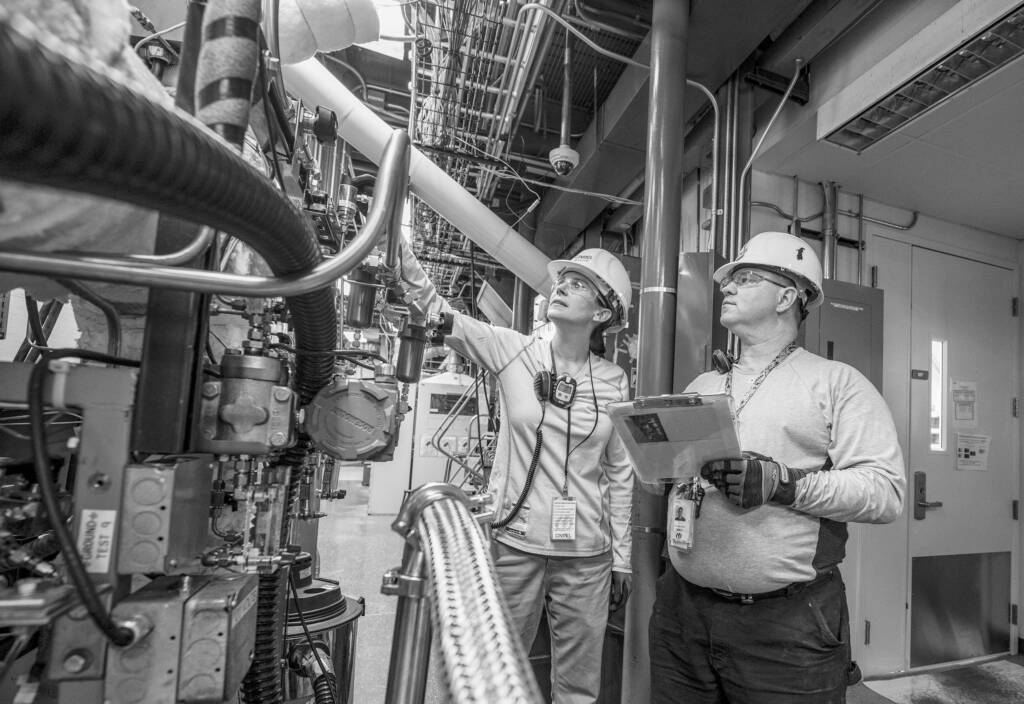

Some Use Cases…
Here are a few real-life cases illustrating the application of 3D scanning and modeling in the field of industrial maintenance:
Conclusion: 3D, the new ally of maintenance!
3D scanning and 3D reconstruction are powerful technologies that bring numerous benefits to industrial maintenance.
By enabling detailed visualization, precise planning, and comprehensive documentation, these technologies optimize maintenance operations, reduce downtime, and improve collaboration among teams.
They now play an increasingly important role in the field of maintenance.